The internet is our gateway to a world’s worth of resources and information, but there will come a time when that connection fails. In this article, we’ll explore how to troubleshoot network connectivity and outline the exact steps to your devices back online.
Some of the most common reasons network connectivity fails are because:
- The network adapter has failed
- Hardware failure on the network
- A network connection has been lost
- Faulty network cables
- Clashing IP Addresses
- Network gear that has been misconfigured
- Network adaptor that has been misconfigured
You’ll be up and running in no time if you follow these network troubleshooting guidelines.
Network Performance Issues
Using an end-to-end solution to continually monitor network performance is the quickest and most accurate approach to discover network issues. Monitoring the performance of your whole network, from LAN to WAN, is known as end-to-end performance monitoring.
The ability of a network to exchange data between devices in a specific period is referred to as bandwidth. Higher bandwidth provides for quicker data transfer and the simultaneous connection of more devices. Congestion occurs when someone or something takes up all of the available bandwidth by downloading terabytes of data.
Another typical network issue is when devices or hardware equipment aren’t working properly, sometimes due to misconfiguration or redundant configuration. It’s critical to examine your network’s switches and devices regularly to verify they’re in good working order so you can respond swiftly if they’re not. Following are some ways to resolve them:
- Readily discover bad performance, create a network performance baseline. It may be used to track the updates or problems that are causing your system to perform poorly.
- A network monitoring system that measures defects on all network interfaces and sends warning signals in the event of possible difficulties is a simple approach to monitoring cables on a damaged connection.
- Ensure that all of your devices are updated. Timely replacement of outdated devices and hardware equipment is essential. When you install any new device to your network, make sure you test them and make sure they’re configured correctly.
DNS Problems
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a database that maps domain names to IP addresses. Every website on the internet has its IP address, and computers may use their IP addresses to connect to other computers and lookup websites. The inability to access the internet or specific websites can have a major impact on your business. They can be resolved by using the following steps:
- If you have wired connections, make sure everything is plugged in properly. If you are on a wireless network, make sure your Wi-Fi is on and you are connected. Make sure your router is plugged in and functional.
- Wait a minute before turning it back on again and wait until the indicator lights stop blinking before trying to connect.
- In some cases, a virus may be blocking internet access. In this case, you may have bigger issues to deal with before you address IP Connectivity.
If this basic troubleshooting doesn’t help, then it’s time for in-depth troubleshooting. Following are some of the problems that might be causing the blockage:
- TCP/IP settings control how your computer interacts with others. You could have recently updated these settings and attempted to manually enter them. Find “Manage network connections” in your computer’s networking or control panel. Find and click on both IPv6 and IPv4 “Properties” under “Local Area Connections,” “Properties.” Make sure “Obtain an IP address automatically” and “Obtain DNS servers address automatically” are both checked.
- Your computer’s DNS cache is where it stores networking information from previous visits and attempts to connect to online sites. The cache can get corrupted as a result of incorrect data. Enter ipconfig /flushdns into the command prompt to flush, or clear, this cache. The DNS cache will have to renew the DNS information the next time you visit a website.
- Is your website address functional but taking you to an unfamiliar site? It’s most possible that you neglected to renew your domain name. It happens to the best of us—in 2015, Google forgot to renew “google.com,” and the domain was briefly lost. Your best hope is to contact the registrar as soon as possible after the domain expires, as many will wait 20 to 30 days before auctioning it off.
IP Address Conflicts
Network connectivity problems are frequently caused by IP address disputes. When two devices on your network share the same IP address, this can happen. As a result, the devices are turned off or unplugged from the network. These conflicts are usually caused by configuration problems. For example, an administrator may have allocated the same IP address to multiple devices by mistake. Fortunately, this problem may be resolved with a few troubleshooting steps.
- There could be many DHCP servers on your network. If that’s the case, double-check that no address ranges on various servers are in conflict. You can compare IP address ranges to look for overlaps if your servers employ automated address allocation. You’ll have to manually check every IP address in your system whether they’re using static allocation.
- The next step is to search for network devices that may have been assigned the same IP address. After that, you can modify the address of one device by reconfiguring it. You might also wish to change the server so that duplicate IP addresses aren’t assigned in the future.
- If none of the foregoing approaches worked, the next step is to seek for the Media Access Control (MAC) addresses of any conflicting devices. You must locate devices that have the same IP address but different MAC addresses. Run the show ip arp command. Next, look for the two IP addresses with different hardware addresses. Doing so will hopefully help you locate the conflicting devices in your network. You can then reconfigure them to resolve the issue.
- Finally, you may wish to locate the switch that is connected to the conflicting devices. You can do this by using your router’s show mac-address-table command. The MAC address for each switch port in your network will be displayed. Alternatively, you might utilize a switch port management application to better locate and track your devices.
Sharing Issues
Due to the large number of components that must be configured correctly, sharing issues are among the most challenging network problems to fix. Conflicts between mixed security settings are the most typical cause of sharing issues. Even various versions of the same operating system can have slightly different security mechanisms, making workstation interconnection challenges. We can cure sharing problems most efficiently by drilling down through the possibilities in this order:
- Ascertain that the essential services are operational. The server, TCP/IP NetBIOS Helper, workstation, and computer browser services must all be running on Windows platforms. Samba is the major component necessary to share files with Windows computers on Linux PCs.
- Examine your firewall (s). It’s fairly typical for a workstation’s firewall to be set to block file and printer sharing traffic, especially if a new antivirus program with its firewall is installed. Hardware firewall issues can also exist, so make sure routers or controlled switches are passing share traffic within the subnet.
- Ascertain that all workstations are connected to the same subnet. This issue is more common on complicated networks, although even basic networks can have static-IP equipment with an incorrectly set subnet. As a result, exterior traffic will flow normally, while interior traffic will encounter unforeseen obstacles.
- File and Printer Sharing for Microsoft Networks, Client for Microsoft Networks, and NetBIOS over TCP/IP must be enabled on all Windows network devices.
- After all of the above checks have been completed, it’s time to look at the most likely problem, permissions. Multiple layers of access are necessary, each with its interface within the operating system. Check for Incorrect NTFS permissions, Network Type set to Public, incorrectly configured HomeGroup and Systems configured within the wrong workgroup or domain.
Configuration Issues
Network connectivity problems are generally caused by recent system changes. New devices and programs installed in your system, for example, could have been misconfigured. The following steps can help in troubleshooting these issues:
- We recommend that you keep track of your device configurations so that you can compare new and older versions. If you’re using a Cisco router, you can preserve your IOS configuration with the archive config command.
- You can use a regular filename and location. The name of every file saved to this place will be the same. However, a new value will be added automatically (e.g., filename1, filename2, etc.).
- Let’s say you wish to learn more about the files in your configuration archive. You’ll need to use the show archive command in this situation.
- The show archive differences command can be used to compare two configuration files. A list of discrepancies between the two files will appear. A plus symbol (+) indicates that a configuration setting is included in filename2 but not in filename1. A minus symbol (-) denotes a feature that is present in filename1 but absent in filename2.
- You can change a variant in your current configuration with one of your older files from your archive if you find one. Use the configure replace command to accomplish this.
- This will make any necessary changes to the current running configuration to replace it with the contents of the supplied configuration file, which is expected to be a complete configuration rather than a partial configuration. If you’re sure you want to go forward, enter Y. Your device or application will now return to its previous state, reversing any recent configuration changes.
Network Problem Troubleshooting Software
Troubleshooting network connectivity problems manually can be tedious and cumbersome at times, especially for people who are not aware of the commands. Hence, it is advisable to use dedicated software that is available for these purposes.
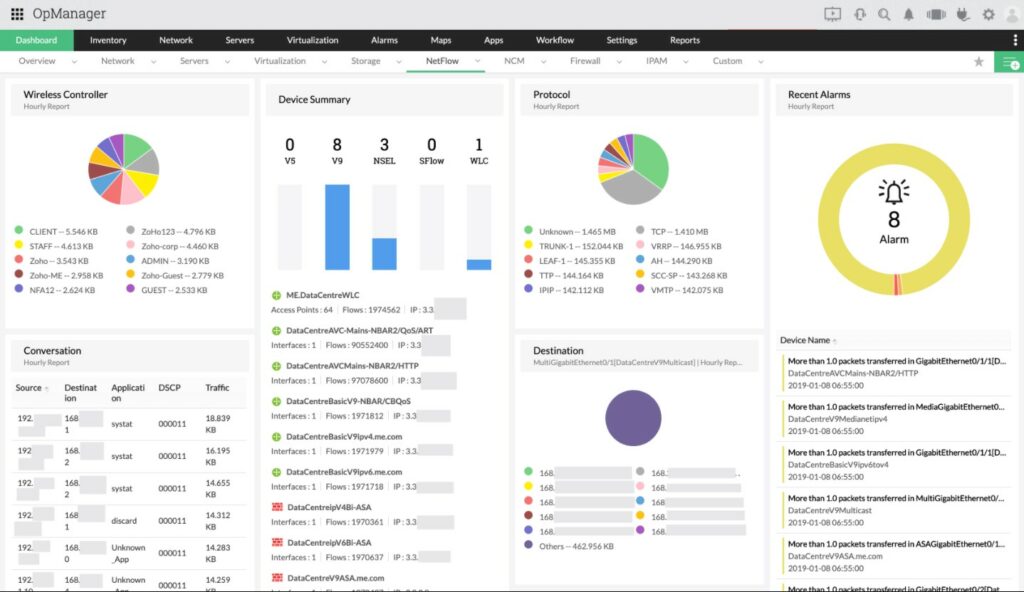
ManageEngine OpManager – FREE TRIAL
ManageEngine OpManager provides robust NetApp monitoring capabilities, including real-time performance tracking and proactive troubleshooting to ensure seamless network operations.
Key Features:
- NetApp Performance Monitoring: Real-time monitoring of NetApp storage systems ensures optimal performance and quick issue resolution.
- Storage Utilization Insights: Provides detailed insights into storage utilization to help manage and optimize storage resources effectively.
- Capacity Planning: Helps in forecasting future storage needs based on current usage trends, aiding in proactive planning.
- Detailed Reporting: Generates comprehensive reports on NetApp performance, usage, and health for better decision-making.
- Threshold-Based Alerts: Customizable alerts notify you of any issues or performance drops in your NetApp storage systems.
- Automated Workflows: Automates routine tasks and responses to common issues, increasing efficiency and reducing manual effort.
- Unified Dashboard: Displays all critical NetApp metrics in a single, easy-to-navigate dashboard for quick access and overview.
Why do we recommend it?
ManageEngine OpManager is highly recommended for its robust NetApp monitoring capabilities, providing real-time insights and detailed reporting that help maintain optimal storage performance and facilitate proactive management.
ManageEngine OpManager provides proactive monitoring, allowing you to detect storage performance issues before they become serious threats. It offers precise capacity planning by monitoring NetApp disk utilization, ensuring accurate forecasting and preventing data capacity overshoots. The tool’s real-time performance monitoring and troubleshooting capabilities help reduce downtime and improve uptime by quickly addressing storage-related issues.
Who is it recommended for?
This tool is ideal for IT administrators and storage managers who need comprehensive monitoring and management of NetApp storage systems, ensuring efficient resource utilization and timely issue resolution.
Pros:
- Comprehensive Monitoring: Offers extensive monitoring of NetApp systems, covering all critical performance metrics.
- Real-Time Alerts: Immediate notifications for performance issues help in quick problem resolution.
- User-Friendly Dashboard: The unified dashboard makes it easy to view and manage all NetApp metrics in one place.
- Automated Task Management: Automates routine tasks, saving time and reducing manual intervention.
Cons:
- Steep Learning Curve: Users may need time to fully understand and utilize all features effectively.
Download a 30-day free trial.
Conclusion
Poor network connectivity can lead to poor performance, slow internet speeds, and downtime for your organization. High bandwidth utilization, IP address conflicts, and device setup mistakes are all potential reasons for network troubles.
These issues need to be diagnosed correctly so that they can be corrected for efficient connectivity. To diagnose these issues more effectively, you can utilize advanced. You can spot problems and rectify them before they have a detrimental impact on your network with the help of interactive maps, proactive alerts, and automated maintenance tasks.
Troubleshoot Network Connectivity FAQs
What are some common causes of network connectivity issues?
Common causes of network connectivity issues include misconfigured network settings, faulty network hardware, software bugs, and interference from other devices or networks.
How do you begin troubleshooting network connectivity issues?
The first step in troubleshooting network connectivity issues is to identify the scope of the problem and gather information about the affected devices and network configuration.
What are some network tools that can help with troubleshooting?
Network tools that can help with troubleshooting include ping, traceroute, netstat, and Wireshark.
How do you use ping to troubleshoot network connectivity?
Ping is a tool that sends a small packet of data to a remote device and measures the time it takes for the device to respond. You can use ping to test basic connectivity between devices on a network.