New OS and software vulnerabilities are constantly being identified. Battles with bugs and defects are endless. New features and capabilities mean progress, and progress doesn’t stop. What does this all mean for the common IT Administrator? Patching, patching, patching.
Implementing a patch management program can significantly reduce the risk of cyberattacks by up to 85%, according to a study by the Center for Internet Security (CIS).
Here is our list of the best patch management tools:
- NinjaOne Patch Management – EDITOR’S CHOICE Formerly NinjaRMM – a patch manager as part of a cloud-based platform of administration tools created for managed service providers. Start a 14-day free trial.
- SuperOps RMM Patch Management – FREE TRIAL A cloud-based platform that includes a patch management module to update endpoints running Windows. This platform also offers a PSA package. Get a 14-day free trial.
- ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus – FREE TRIAL An automated patch manager for Windows, Windows Server, macOS, and Linux. Installs on Windows Server and Linux. Download a 30-day free trial.
- Atera – FREE TRIAL This SaaS platform provides remote monitoring and management services in editions for IT departments and managed service providers. The patch manager automates that patch update process and is hosted in the cloud. Get a free trial.
- N-able N-sight Patch Management – FREE TRIAL A cloud-based platform of tools for remote monitoring and management that includes a patch manager.
- ESET Protect MDR This Managed security service provides technicians to look after your system’s security, including vulnerability scanning and patch management. Endpoint agents run on Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, and Android.
- SecPod SanerNow Patch Management This cyber-hygiene endpoint management system includes a patch manager that is linked to a vulnerability scanner and an asset manager. This is a cloud platform.
- Syncro This cloud-based package of tools for managed service providers includes a patching service for computers running Windows.
- SolarWinds Patch Manager A patch automation system that covers Windows and Windows Server plus a long list of software brands, including Microsoft, Adobe, and Google. Installs on Windows Server.
- Ivanti Patch for Endpoint Management This patch manager is an add-on for the Endpoint Management platform from Ivanti and it manages devices running Windows, macOS, and Linux. Runs on Windows Server.
- GFI LanGuard A patch manager to automate updates to Windows, Windows Server, macOS, and Linux. Installs on Windows Server.
Patch management tools can automate and streamline the process, enabling administrators to manage patch deployment across multiple systems and track the status of each patch to ensure that all systems are up-to-date and secure.
One might say WSUS (Windows Server Update Services) by Microsoft can handle these hotfixes and patches.
True, but if you’ve ever used WSUS, you know it’s overly cumbersome to use, riddled with pesky caveats, and most importantly: only works with Microsoft product updates.
What about SCCM (System Center Configuration Manager) by Microsoft?
SCCM is WSUS on steroids, built for the Enterprise. However, and by no secret, SCCM is a beast to manage, with massive administrative overhead. This offering by Microsoft is robust, but typically only manageable by large organizations with teams dedicated to such a role.
The Best Patch Management Tools & Software
Patch management solutions should be scalable, easy to use, and cover a wide variety of vendor software. Some are purely standalone systems, while others offer additional integration with WSUS or SCCM.
Our methodology for selecting patch management tools
We reviewed the market for automated patch management software and analyzed the options based on the following criteria:
- A system that discovers all installed packages and creates an inventory
- Automated patch availability searches
- Scheduling for automatic patch rollout
- The ability to order activities to account for patch dependencies
- Wake-on-LAN and restart capabilities
- A free trial or a demo that enables an assessment before purchasing
- Value for money from a patch manager that also provides software management functions
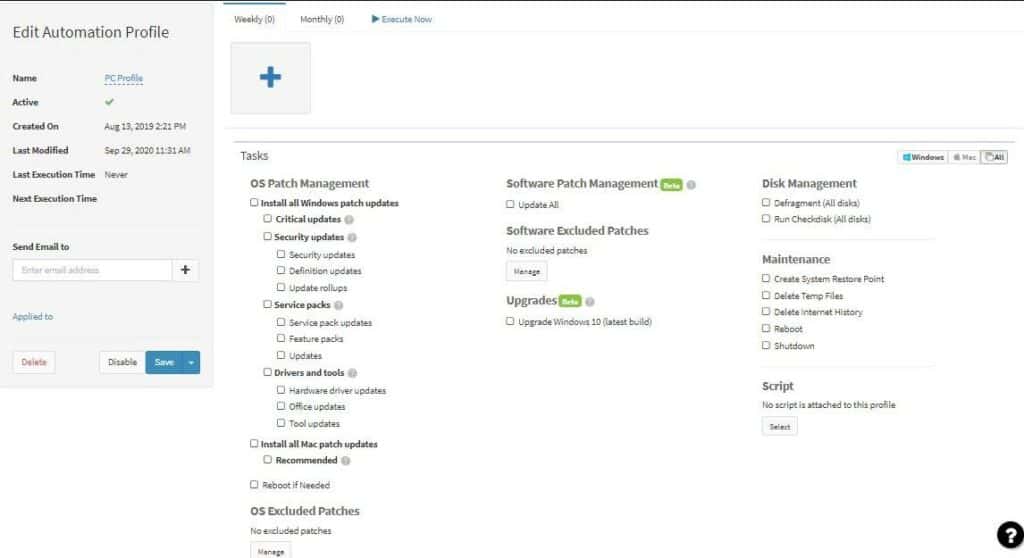
1. NinjaOne Patch Management – FREE TRIAL
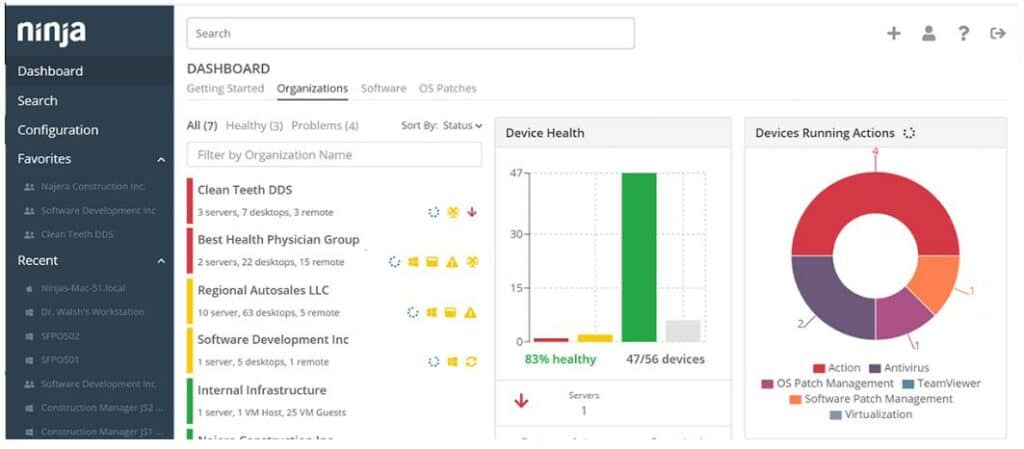
NinjaOne – formerly NinjaRMM – is a remote monitoring and management (RMM) platform. It supplies all of the tools that technicians need in order to support IT services. This collection of software is particularly needed by managed service providers (MSPs) but it could also be used by IT departments that manage a number of remote sites. The package of services in NinjaOne includes a patch manager.
Key Features:
- SaaS package
- Operates on Windows and macOS
- Designed for MSPs
- Software inventory
Why do we recommend it?
NinjaOne Patch Management is part of a platform of remote monitoring and management tools. The platform includes a Help Desk ticketing system so it is an ideal package for an IT support team. The patch manager is able to update Windows, macOS, and Linux plus software packages.
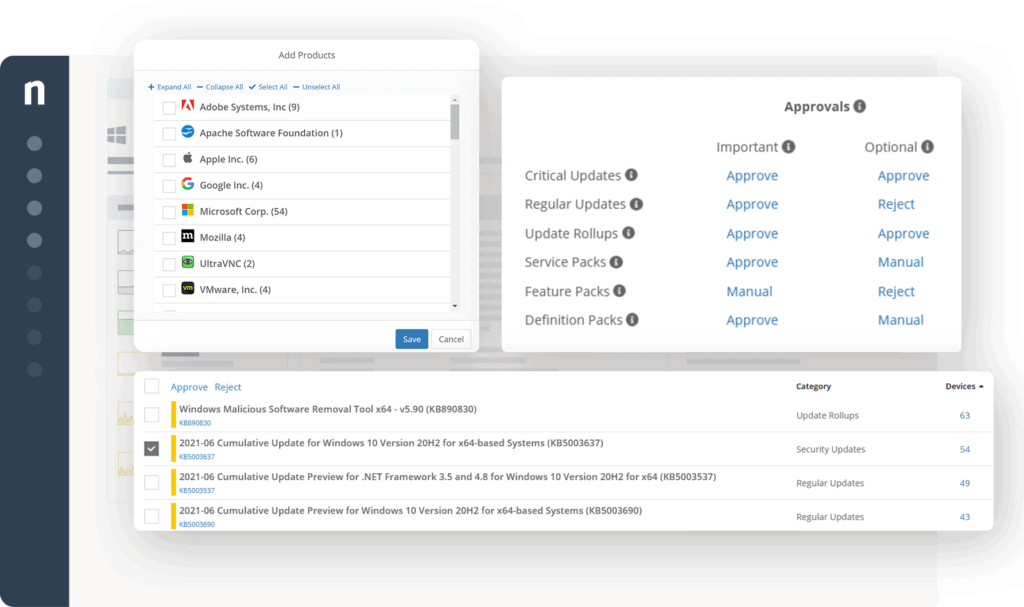
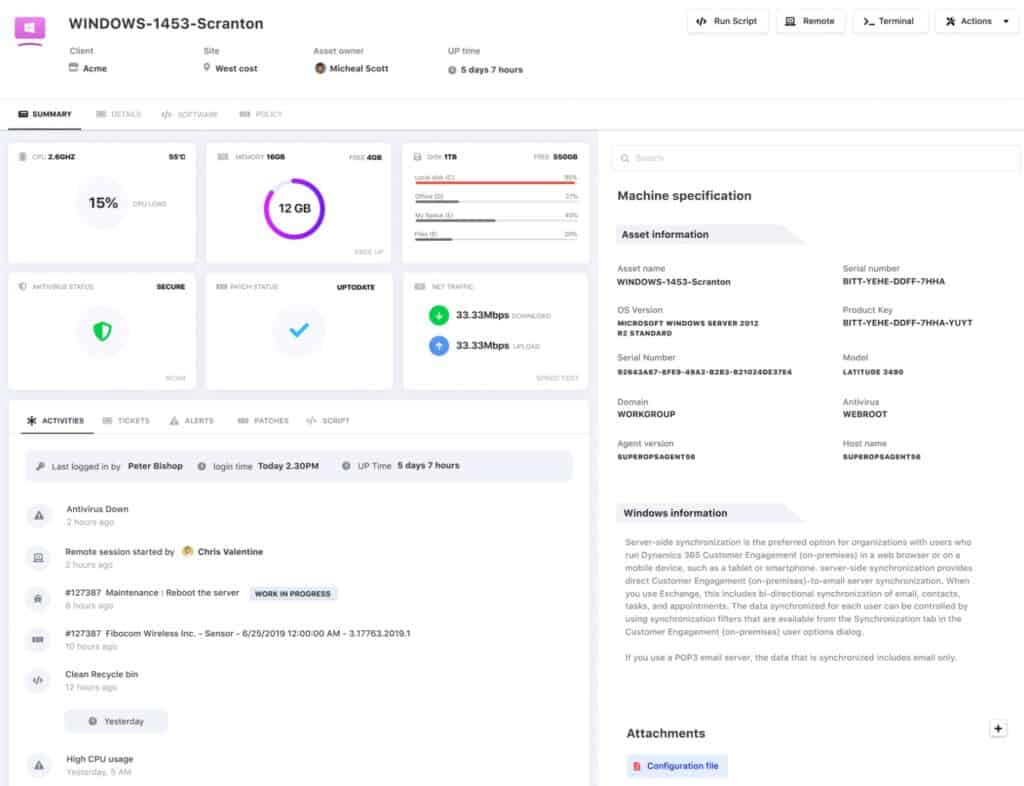
The NinjaOne patch manager watches over Windows and macOS operating systems plus system services and hardware drivers. It is also able to manage the statuses of 135 software packages. The tool notes the versions of each OS and software package, which indicates their patch statuses.
With a registry of software and operating systems as its reference source, the patch manager watches out for the availability of patches from suppliers. Whenever a patch is made available, it copies over and stores the installation pack. This is then made available for review in the NinjaOne console. Operators can schedule patches for out-of-hours installation and get them installed on all candidate devices or target one or two systems individually.
Patches can be held back for investigation, which means that other available patches are not held up just because one in the list of available updates needs consideration. Patches can also be applied individually on demand. The service can be allowed to automatically implement a system reboot when required by the patch.
Who is it recommended for?
The main customer base of the NinjaONe platform lies with managed service providers (MSPs). However, It departments could also use the system for in-house system management tasks. The service includes cost-saving automation measures and is hosted on the NinjaOne cloud system so your own technicians don’t need to maintain the NinjaOne software.
Pros:
- Can silently install and uninstall applications and patches while the user works
- Patch management and other automated maintenance tasks can be easily scheduled
- Platform agnostic web-based management
Cons:
- Lacks support for mobile devices
One cannot discuss industry leaders without noting NinjaOne’s repeated accolades on G2 in its niche. NinjaOne is a cloud-based system so there is no need to install or maintain the software. The system is charged for on a subscription with a rate per monitored device. You can find out more about pricing with a direct quote. Start a 14-day free trial.
EDITOR'S CHOICE
NinjaOne is our top pick for a patch management tool because this is a full remote monitoring and management platform that provides many other functions as well as patch management. Endpoint monitoring and management features create software profiles that lead to license management and automated patch management. This chain of endpoint and software management services applies to operating systems and software packages. The service will queue up patches to be applied at the next maintenance window – a calendar that you set up in the console. This system is suitable for use by IT departments and managed service providers.
Download: Start 14-day FREE Trial
Official Site: https://www.ninjaone.com/freetrialform/
OS: Cloud-based
2. SuperOps RMM Patch Management – FREE TRIAL
The Patch Management service of SuperOps RMM is part of a SaaS platform that also includes a PSA system. The combination of these two packages provides comprehensive services for MSPs.
The SuperOps system is customizable. The platform includes a lot of automated processes but the user can adapt these or create new automation procedures with the platform’s scripting language.
Key Features:
- SaaS RMM and PSA package
- Manage WFH endpoints
- Patching for Windows
Why do we recommend it?
SuperOps RMM Patch Management is a cloud-based service that enables a single IT office to support endpoints on multiple sites. The patch manager is automated, which means that technicians don’t need to spend any time researching the path statuses of all of the software on the endpoints that they manage.
The Patch Management tool is also adaptable because it includes essential automated processes but also presents options on how the system will operate.
The basis of the Patch Management service is the associated Asset Management module in the SuperOps platform. This detects all desktops and laptops connected to the monitored network. It then cans through those that run the Windows operating system and documents its software, creating an inventory.
The Patch Management system regularly check with the suppliers of the software under management for updates and patches. The system copies down the installers for encountered patches and then lists them as available in the system console.
Who is it recommended for?
SuperOps RMM is suitable for use by managed service providers and IT departments. The company also offers a combined RMM and PSA package, which would only be of interest to MSPs. The RMM package is priced per technician and SuperOps claims that its system will enable each technician to support 150 endpoints.
Pros:
- Highly customizable – great for companies looking to build their own SOPs
- Is a hybrid RMM/PSA solution
- Flexible cloud-based product
- Great option for MSPs and larger in-house teams
Cons:
- Would benefit from a longer trial
You need to define a calendar of maintenance windows in the dashboard and then decide whether the system will roll out patches automatically or wait for an operator to approve each patch. Start a 14-day free trial download.
3. ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus – FREE TRIAL
Managing software Updates on your desktops and servers is a no-brainer. But why stop there?
Wouldn’t it be nice to have a full picture of your windows server and device environment to include desktops, laptops, servers, linux and mac systems!
Key Features:
- Software distribution option
- Patching for Windows, Linux, and macOS
- Patch tester
Why do we recommend it?
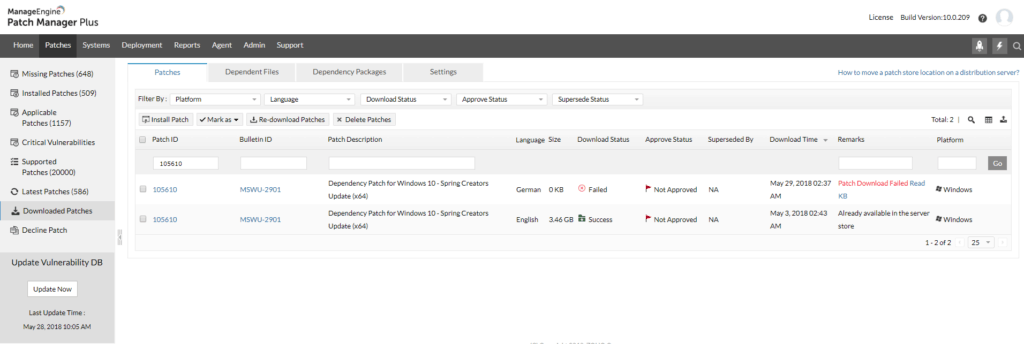
ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus will patch operating systems and software. The tool is able to manage endpoints running Windows, macOS, and Linux. ManageEngine gathers any available patch installers, tests them, and then stores them in the cloud. Each Patch Manager Plus installation then has only one library to refer to.
This is exactly what ManageEngine is attempting to accomplish with it’s Patch Management tool, Patch Manager Plus.
The solution supports updating Windows, Mac and Linux to give you a fully thought out solution for all your update issues.
From a patch management perspective, this Software automates patch deployments on Windows, Linux and Mac, including numerous third-party applications that run on top.
Built-in templates for package creation make it easy to create your own software distributions and manage the install/uninstall process.
Power management capabilities cannot only save you money on utility costs, but it can also ensure that your systems are online to be patched.
Additional features of this tool include some of the following:
- Free Edition of this tool is great for SMBs
- The Pro & Enterprise Versions are Full-Fledged Systems for Medium to Large Organizations
- Update all Endpoints on Linux, Windows & Mac Servers and Devices (including Laptops and Desktops)
- Deploy Windows Service Packs automatically!
- Robust & thorough Reports
- Detect, Test, Deploy and Approve Patches
- 2FA Capabilities
- Ability to Add Distribution Server for Bandwidth Optimization
- Role Based Administration for Network Admins & Engineers!
- and many more features!
Who is it recommended for?
This patch manager is available in three editions. The Free edition is limited to updating 20 workstations and five servers, which is suitable for use by small businesses. The two paid versions are designed to manage a single site or a WAN. The system is available as a software package for Windows Server or as a SaaS platform.
Pros:
- Flexible deployment options across multiple platforms
- Can be installed on both Windows and Linux platforms, making it more flexible than other on-premise options
- Offers in-depth reporting, ideal for enterprise management or MSPs
- Integrated into more applications than most patch management solutions
Cons:
- ManageEngine is a feature-rich platform that takes time to fully explore and learn
Download a 30-day free trial.
4. Atera – FREE TRIAL
Atera is an IT management software to support managed service providers (MSPs) and IT Departments. The technician tools included in this cloud-based service include a patch manager. This is a multi-tenanted system so one technician can orchestrate patch management for several clients on the same console. The automated processes in the tool make light work of patch identification and rollout as well as advanced patch management such as exclusion and postponement settings.
Key Features:
- Maintenance windows
- Unattended and attended remote access
- Runs scripts for task automation
- Software installation
- Patching for Windows and macOS
Why do we recommend it?
The Atera platform is hosted in the cloud so its console can be accessed from anywhere through any standard Web browser. Its automated patch manager includes a launcher for other tasks as well, such as standard maintenance tasks. You can also use the interface to launch your own custom scripts on a schedule.
An automated patch management tool in the bundle can also be used to install software and run task automation scripts. The patch management system scans devices within a profile and identifies the versions of each. This enables the patch manager to search for patches that are available for those versions to get those systems up to date.
Once patches are queued for roll-out, an administrator can choose to hold back one or many pending further investigation. This utility means that the need to verify one patch doesn’t prevent all other urgent patches from being applied. Patches can be postponed for automatic approval after a certain amount of time or excluded indefinitely until you manually apply approve the patch.
Patches can be applied in bulk or individually and on a schedule or on demand. OS patch management includes critical, security, service packs, drivers, and tools (including Microsoft Office and drivers such as Java and Adobe), as well as Mac OS updates and software patches.
Atera is available in versions for IT departments and managed service providers. These are the two types of teams that regularly need to manage software, so creating two different editions for the remote monitoring and management system that includes the patch manager was a clever idea. The patch manager will operate on endpoints running Windows and macOS. The full RMM system is offered in different packages that offer packages of system management tools that include a Help Desk ticketing system. Per technician, pricing means that this SaaS platform is scalable and accessible to organizations of all sizes.
Who is it recommended for?
This system is charged per technician, which makes it suitable for businesses of any size. The SaaS platform is available in versions for managed service providers and for IT departments. Both versions have four plans and all editions include the patch manager among their automated system management features.
Pros:
- Minimalistic interface makes it easy to view the metrics that matter most
- Flexible pricing model makes it a viable option for small businesses
- Includes multiple PSA features, great for helpdesk teams and growing MSPs, and large-scale IT Departments
- Can track SLAs and includes a time-tracking option for maintenance tasks
Cons:
- Smaller businesses may not be able to make the most of the diverse features
Starting at $129/technician, the whole Atera system is available in three editions for MSPs: Pro, Growth, and Power and three editions for IT Departments: Professional, Expert, Master. Both solutions also have an enterprise package available upon request. Charges are levied per month per technician. Try Atera on a 30-day free trial.
5. N-able N-sight – FREE TRIAL
N-able N-sight is a cloud-based platform that includes all of the tools that a managed service provider (MSP) or central IT department needs in order to manage software on many sites. The tool is fully automated but it also allows for a variation in the approval and automated rollout process to enable technicians to hold back individual patches in a batch for further investigation.
Key Features:
- Designed for MSPs
- Patches Windows and Microsoft products
- Full RMM package
Why do we recommend it?
N-able N-sight is a remote monitoring and management package that is delivered from the cloud. The service can be accessed through any standard Web browser. The package includes a patch manager that is able to manage devices running Windows, macOS, Linux, and iOS. The platform also provides scripts for automated endpoint management tasks.
The N-sight suite includes an autodiscovery service, which identifies all of the devices connected to the network and creates a software inventory for each. This includes the version numbers for the operating system and software running on each. Those version numbers indicate the current patch version.
The tool polls suppliers for updates and copies the installers over whenever they become available. A scheduler in the patch management service allows technicians to time patch rollout to occur overnight, thus minimizing disruption.
Other features in this patch management system include status reports for completed rollouts. Individual patches that failed to apply can be investigated and run again on-demand or on a schedule.
Who is it recommended for?
N-able N-sight is designed for use by managed service providers. The package also includes a Help Desk ticketing system and so also provides technician team management functions. The tool aims to support 100 endpoints for each technician. Pricing is per technician, which makes the system suitable for any size of business.
Pros:
- Highly scalable cloud-based platform
- Flexible pricing (great for small and growing MSPs)
- Offers numerous white-label products that make it easy to expand your offerings
- Integrates well with N-able RMM
Cons:
- Would like to see a longer trial period
Get a 30-day free trial of N-able N-sight with its Patch Manager.
6. ESET Protect MDR
ESET produces a range of cybersecurity packages under the Protect name. These editions start with an on-device anti-virus system, which is available for Windows, Linux, macOS, iOS, and Android. This service performs threat detection and response for each device and also uploads activity reports to a cloud-based console. Higher plans add on threat hunting on the cloud, a vulnerability scanner, and a patch manager.
The vulnerability manager sets up the patch manager when it discovers out-of-date software. It also produces guidance on manual changes needed to device settings. Responses to detected threats can be automated. However, there will always be borderline cases that require expert judgment. If you haven’t got a cybersecurity expert on staff, you will need the ESET Protect MDR package.
Key Features:
- Threat detection and response
- Endpoint protection for computers and mobile devices
- The services of cybersecurity experts
Why do we recommend it?
ESET Protect MDR is an entire Security Operation Center for a business and it even includes the technicians to manage the software and assess any alerts that it raises. The package provides an automated vulnerability scanner that is linked to a patch manager. This suite reduces the risks of hacker attacks.
The MDR system adds technicians onto the SaaS bundle. So, it includes cybersecurity software, a hosted threat detection system, cloud storage space for metrics, and cybersecurity experts to run the software and act on its findings.
Prospective buyers of the ESET Protect system should assess all of the editions of the service. The basic system provides only the on-device anti-virus system with a cloud console for statistics. The patch manager is included in the top two editions, which are called ESET Protect Complete and ESET Protect Elite.
Who is it recommended for?
This system is designed for businesses that don’t want to run their own cybersecurity department. This strategy is appealing to small businesses and also to larger companies that find it difficult to source experienced cybersecurity technicians. The package also provides email security and endpoint security.
Pros:
- Managed detection and response service
- Connected vulnerability scanner and patch manager
- A hybrid system with on-device elements and a cloud-based module
Cons:
- No free trial
The MDR package is a custom service and its price depends on which of the two upper plans you choose. In order to find out more, you should contact ESET.
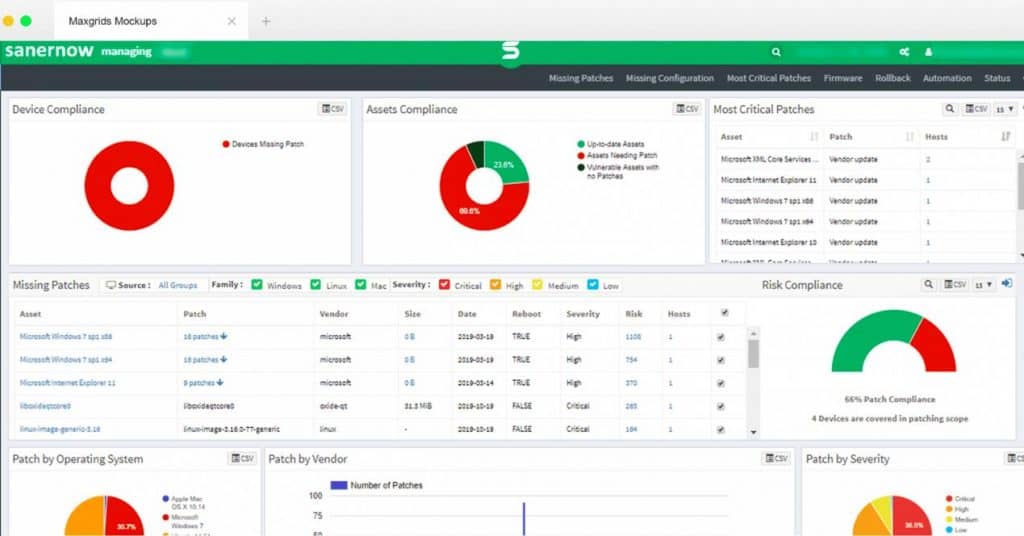
7. SecPod SanerNow Patch Management
SecPod SanerNow Patch Management is a cloud-based cyber-hygiene endpoint protection system that offers the latest automated security patches for devices running Windows, macOS, and Linux.
This package of security services centers on a vulnerability scanner. This system identifies configuration weaknesses and feeds through to an automated patch manager. The patch manager in SecPod SanerNow is managed from the SaaS console, which can be accessed from anywhere through any standard Web browser.
Key Features:
- Patches Windows, macOS, and Linux
- Manages 400 software pacakges
- Rapid patch availability detection
Why do we recommend it?
The SecPod SanerNow Patch Management solution scans your endpoints and compiles a software inventory. The version numbers on each package indicate their patch statuses and the SecPod system uses this to look for newer patches that need to be installed. Patches are applied automatically out of office hours.
The service takes a list of software from the asset manager module, looks at the results of the vulnerability manager, and then polls software supplier sites from available updates. It also keeps regular tabs on patch availability at the suppliers of the operating systems running on the monitored network’s endpoints.
The patch rollout process is automated. However, you set up maintenance windows in the console to indicate allowed times for patches to be applied. In emergency situations, it is possible to override the automation and initiate an on-demand patch installation.
The dashboard for the patch manager shows pending patches and a patch history with termination statuses. This enables you to investigate the reasons why some patches failed to apply, make system adjustments, and then let them be rerun at the next maintenance window.
Additional features of this tool include some of the following:
- Data privacy compliance reports
- Patch termination status reports and rollout logging
- An associated automated vulnerability manager
- Automated patch management workflows
- Cloud-based console available from anywhere through any standard Web browser
- Patch rollout scheduling that includes pre-requisite checks and update version ordering
- Support for Windows, macOS, and Linux
- Patch severity detection and prioritization
- Options for manual patch rollout launch
- Patch event logging and termination status reporting
Who is it recommended for?
This system is a good choice for multi-site businesses that run a central IT operations department. The system will patch Windows, macOS, and Linux plugs more than 450 software packages. The company doesn’t publish its proxies and that will deter small businesses from enquiring about the patch manager.
Pros:
- Offers ITAM capabilities through a SaaS product, making it easier to deploy than on-premise solutions
- Features cross-platform support for Windows, Mac, and Linux
- Can automate asset tracking, great for MSPs who bill by the device
- Can scan for vulnerabilities, making it a hybrid security solution
Cons:
- Better suited for larger environments
Start a 30-day free trial.
8. Syncro
Managed service providers have to cover all of the system operations tasks for the companies that they work for.
This requires a set of remote monitoring and management tools and the cloud platform provides these along with the professional services automation (PSA) bundle that helps the managers of the MSP run the business.
The Syncro RMM package includes a patch manager for computers running Windows.
Key Features:
- Variable security policies
- Automated patching
- Operating systems and software
Why do we recommend it?
Syncro is a very large package of tools and the patch manager is one of them. The wider RMM package is able to monitor and manage endpoints running Windows and macOS. The full bundle of tools includes contracts management and invoicing plus a Help Desk ticketing system, team management features, and role-based consoles.
The technician tools in the Syncro bundle provide all of the systems that a technician needs to run a remote network, including remote access to support endpoints.
The RMM looks after endpoints running Windows and macOS. The system supports the creation of task automation scripts.
Syncro provides a library of user-contributed free automation scripts that improve the productivity of MSP technicians.
The endpoint scanner creates a software inventory that includes version numbers. This indicates patch statuses. The system will automatically poll for patch availability.
This system provides a range of patch strategies, including the possibility to run a patch installation manually.
Additional features of this package include:
- Wake-on-LAN for out-of-hours patching
- Remote shutdown after the patch run
- Option to patch specific endpoints or all on the site
- Patching for Windows
- Updates for Microsoft software
- Updates for third-party software
- Automation for pre and post update systems settings changes
- A package of automated monitoring systems
- Alerts for system problems
Who is it recommended for?
The Syncro package is designed for use by managed service providers. While many RMM packages can be used by IT departments for in-house system support, the PSA features in the platform would only be of interest to MSPs and the two bundles are indivisible.
Pros:
- A cloud-based package that can unify a geographically scattered support team
- Web-based consoles for each role
- Automated patching that rolls out at the next available patch window
- A scheduling system that sets up the definition of maintenance periods
Cons:
- The system can’t patch Macs
Access a 14-day free trial.
9. SolarWinds Patch Manager
SolarWinds’ award-winning solution, Patch Manager (PM), is well-rounded and a breeze to work with.
Alongside Microsoft patching, SolarWinds PM includes support for a wide variety of 3rd party applications, simplifying and centralizing the entire patch process, from download, to publish, to patch.
Key Features:
- Patch and install
- Create install packages
- Patch activity logging
Why do we recommend it?
SolarWinds Patch Manager is an adaptation of the Windows SCCM system. It enables the regular Windows service to install third-party software instead of its usual restriction of just installing and patching Microsoft products. This system is delivered as an on-premises software package for Windows Server.
Integrating with WSUS and Microsoft update agent, SolarWinds PM can automatically patch systems based on custom schedules. Have SCCM deployed?
No problem, as SolarWinds Patch Manager cleanly integrates with SCCM, supplementing your installation with value-adds such as on-demand patching, filtered views, notifications, and more. Create custom packages using a simple point-and-click wizard (no scripting knowledge required!).
The Patch status dashboard is consistent with what you’d expect from SolarWinds, providing familiarity, especially if you’re already using SolarWinds for Server or Active Directory monitoring. Built-in reports determine the status of patches and demonstrate to auditors that systems are patched and compliant.
I’ve seen this solution implemented and countless environments. It’s absolutely outstanding and continues to be a top choice in my book.
Who is it recommended for?
This package has high volume capabilities and so large companies will get the best value for money from it. The tool is only able to manage software on endpoints that run Windows, so companies that have a mix of operating systems on-site will need to look elsewhere for a patch manager.
Pros:
- Simple dashboard makes it easy to track and visualize patches and their progress, even on larger networks
- Integrated directly with SCCM for a smoother patch deployment
- Supports a wide variety of third-party patching options
Cons:
- The tool is very enterprise focused, may not be the best option for home labs or small networks
10. Ivanti Patch for Endpoint Management
LANDesk Management Suite has been taken over by Ivanti and is now called Ivanti Endpoint Management. Ivanti Patch for Endpoint Management is an add-on module for that unified endpoint management (UEM) suite.
This system operates as a vulnerability scanner through its regular checks for patch availability.
Key Features:
- Unattended operations
- Patches Windows, Linux, and macOS
- Part of a security suite
Why do we recommend it?
Ivanti Patch for Endpoint Management is an add-on for a security package and it includes a vulnerability scanner. The system will scan endpoints running Windows, macOS, and Linux. The tool will update operating systems and software. This is an automated system that will install patches on a schedule and also provides a manual launch option.
Ivanti patch management add-on provides patch gathering for operating systems and third-party software packages. It specializes in managing devices running Windows, macOS, and Linux.
Ivanti maintains a library of the latest patches for well-known software systems and the implementation of Ivanti Patch download update installers from that library rather than directly from the supplier. The Ivanti platform tests and verifies each patch before making it available for download.
Any patch manager works best out of office hours because the update process can temporarily disrupt the operations of the software that it patches. So, the Ivanti system is based around a scheduler, you give it a calendar of maintenance windows and the system will apply patches at the next available period. The system will wake up devices and perform restarts where necessary.
Who is it recommended for?
This is an extra unit that adds on to the Ivanti Endpoint Manager, which is a unified endpoint management (UEM) package. So, the UEM is the primary product and the customer base for the patch manager will come from that pool of users. This is a software package that runs on Windows Server.
Pros:
- Integrates into Ivanti Endpoint Management
- Pre-verified patch library
- Runs out of office hours
Cons:
- You must be running Windows Server to install the package
- Not a standalone product
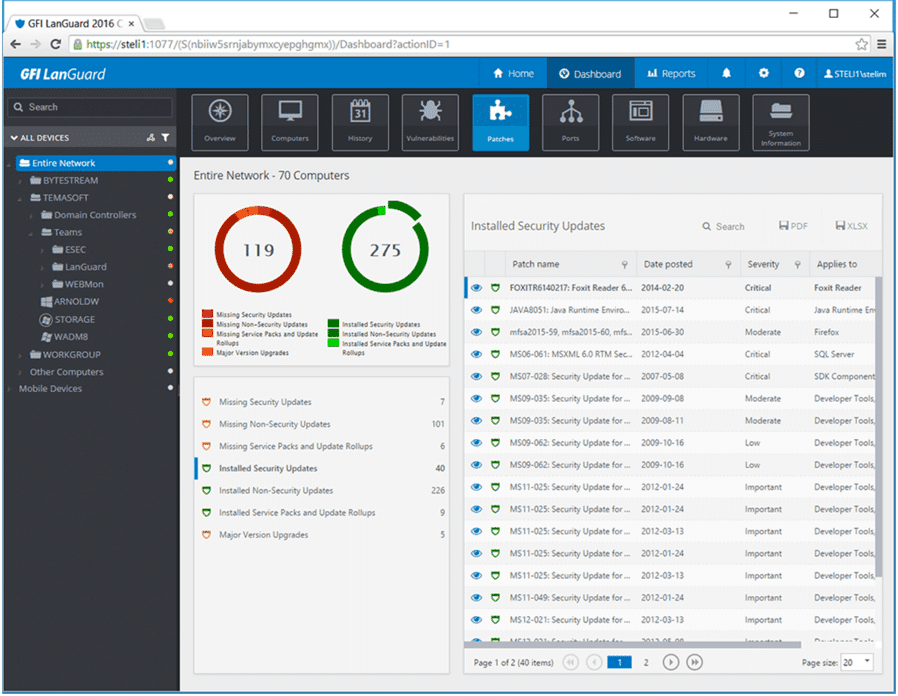
11. GFI LanGuard
If I could give an award for best-looking UI, I’d give it to GFI LanGuard. Its clean and non-distracting interface makes it a pleasure to work with.
This solution has been recognized in the industry for its specialized ability and commitment towards best-in-class solutions for SMBs. GFI LanGuard supports various Operating systems, including Microsoft, Mac OS X, and Linux, and more than 60 third-party applications.
Key Features:
- Device discovery
- Operates on Windows, Linux, and macOS
- Software auditing
Why do we recommend it?
GFI LanGuard is a patch manager and network monitoring system. The package will scan your network and identify all devices. The system creates an IT asset inventory and then scans each endpoint for software. That phase forms the basis for a patch management service. The system updates Windows, macOS, and Linux plus third-party software packages.
Vulnerability assessments help in discovering risks and threat early on, enabling you to automate remediation upon detection. Built-in alerting keeps you up-to-speed with the dynamic environment.
Audits can be stressful, and GFI knows this. Advanced analysis reports detail installed applications, antivirus and other security application status, open firewall ports, file shares, and even application-specifics such as default configurations.
Some additional bonuses I’d like to point out with GFI LanGuard is its change management component, asset inventory capabilities and mobile app. While not necessarily a requirement for patch management, these add-ons are handy and may be something worth checking out if you’re not already incorporating such tools in your environment.
Who is it recommended for?
This system is a comprehensive security service that would be suitable for any size of business. The company doesn’t publish a price list, which is going to make it less appealing to small businesses. Thus an on-premises package that installs on Windows Server.
Pros:
- Multi-platform support for Microsoft, Linux, and Mac
- Includes support for patching other popular third-party applications like Adobe, Java, and Runtime
- Simple, yet effective interface
- Built-in vulnerabilities assessment uses patch information to help gauge risk for security teams
Cons:
- Would like to see more features for scheduling patches
- Could use more up-to-date support for newer third-party applications
Conclusion
We’ll continue updating the list as we find more of the Best Patch Management Software on the Market.
If we missed any, please feel free to send us an email via our Contact page and we’ll be sure to get this post updated immediately!
Patch Management Tools FAQs
Why is patch management important?
Patch management is critical for maintaining the security and performance of computer systems and networks, reducing the risk of cyberattacks, avoiding financial losses, and complying with regulatory requirements.
According to the Ponemon Institute, 60% of data breaches are caused by unpatched vulnerabilities. Failure to patch systems in a timely manner can result in significant financial losses. The average cost of a data breach is $3.86 million.
Additionally, patch management can help organizations comply with regulatory requirements, such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which require organizations to maintain up-to-date software and implement security patches in a timely manner.
How often should patch management be performed?
It is recommended that organizations perform patch management on a regular basis, typically at least once a month. This allows organizations to stay up-to-date with the latest security patches and to address any critical vulnerabilities as they arise.
However, in some cases, more frequent patching may be necessary. For example, organizations that handle sensitive data, such as financial institutions or healthcare providers, may need to patch more frequently to minimize the risk of a data breach.
In addition to regular patching, it is important for organizations to have a plan in place to address critical security patches as soon as they are released. Critical patches are typically released outside of the regular patch cycle and may require immediate attention to avoid exploitation by attackers.
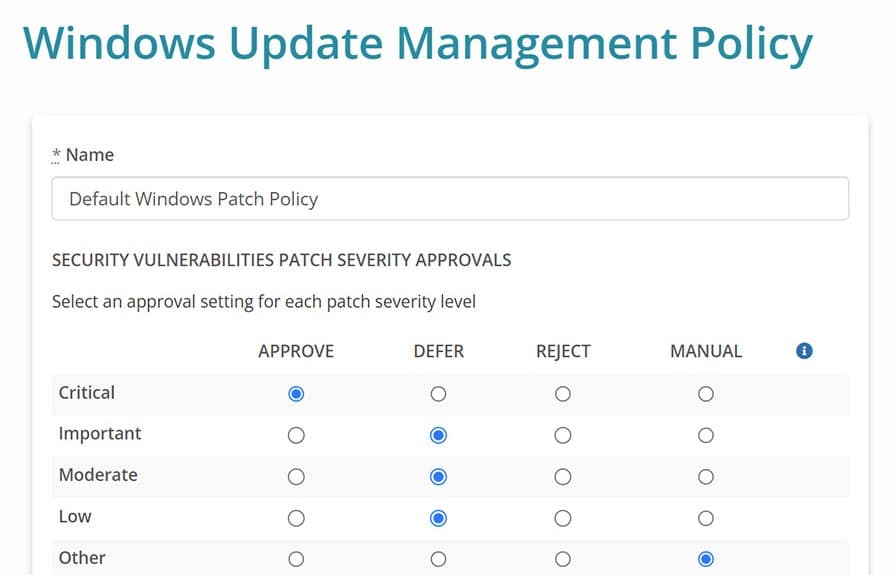
What is a patch management policy?
A patch management policy is a set of guidelines and procedures that an organization follows to manage and deploy software patches across its IT systems and networks. The policy outlines the steps that must be taken to ensure that patches are applied in a timely and consistent manner, and that systems remain secure and up-to-date.
A typical patch management policy will include the following components:
- Roles and responsibilities: specify the roles and responsibilities of each member of the IT team who is involved in the patch management process. This includes identifying who is responsible for patch testing, deployment, and monitoring.
- Patch management procedures: outline the procedures that the organization will follow to manage and deploy patches. This includes procedures for identifying and assessing vulnerabilities, testing and approving patches, and deploying patches to production systems.
- Patch deployment schedule: define a schedule for patch deployment that ensures that patches are applied in a timely and efficient manner, while minimizing disruption to business operations.
- Testing and approval process: outline the procedures for testing and approving patches before they are deployed to production systems. This includes identifying which systems will be used for testing, and how the results of the testing will be evaluated.
- Documentation and reporting: The policy should require that all patch management activities be documented, including patch deployment status, testing results, and any issues encountered during the patching process. This documentation should be used to produce regular reports on patch management activities, which can be used to assess the effectiveness of the patch management program.
What are some common patch management tools?
Common patch management tools include: Atera, Microsoft System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM), IBM BigFix, Ivanti Patch for Windows, and SolarWinds Patch Manager.
What types of software can be managed using patch management tools?
Patch management tools can manage software updates for various applications, operating systems, and devices, including Windows, macOS, Linux, and mobile devices.
How does patch management work?
Patch management works by identifying vulnerabilities, obtaining and testing patches, and deploying patches to affected systems.
What types of vulnerabilities can be addressed using patch management?
Vulnerabilities that can be addressed using patch management include software bugs, security flaws, and compatibility issues.
How often should patches be deployed?
Patches should be deployed as soon as possible after they become available, especially for critical and security patches.
What is the patch management process?
The patch management process typically involves five stages: vulnerability assessment, patch acquisition, testing, deployment, and verification.
Can patch management tools automate the patching process?
Yes, many patch management tools can automate the patching process, which can save time and resources while improving efficiency and accuracy.
What are the risks of not implementing patch management?
The risks of not implementing patch management include increased vulnerability to security threats, poor system performance, and regulatory non-compliance.